生产者消费者
synchronized版
public class cp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread2").start();
}
}
class Data {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void increaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
if (number == 1) {
this.wait();
}
number = number + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decreaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
if (number == 0) {
this.wait();
}
number = number - 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
this.notifyAll();
}
}虚假唤醒问题
我们再加两个线程会怎么样?
public class cp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread2").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread3").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread4").start();
}
}
class Data {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void increaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
if (number == 1) {
this.wait();
}
number = number + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decreaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
if (number == 0) {
this.wait();
}
number = number - 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
this.notifyAll();
}
}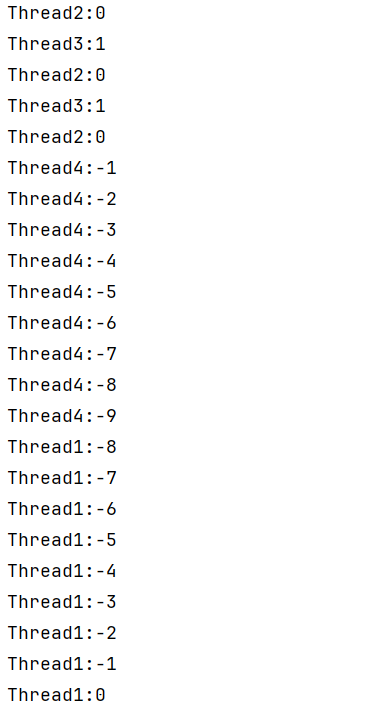
问题出现的原因时我们使用了if判断,只判断了一次,被幻想后即使不符合条件依旧会往下执行,这就叫虚假唤醒,用while即可解决。
public class cp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread2").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread3").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread4").start();
}
}
class Data {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void increaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
while (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
number = number + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized void decreaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
while (number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
number = number - 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
lock版
利用Condition来等待和唤醒
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class cp1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data1 data = new Data1();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread2").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.increaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread3").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.decreaseNumber();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "Thread4").start();
}
}
class Data1 {
int number = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void increaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 0) {
condition.await();
}
number = number + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
condition.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decreaseNumber() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (number != 1) {
condition.await();
}
number = number - 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}利用Condition来精准唤醒指定线程执行顺序
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class cp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data3 data = new Data3();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.printA();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.printB();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
data.printC();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "C").start();
}
}
class Data3 {
private int number = 1;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
public void printA() {
lock.lock();
try {
if (number != 1) {
condition1.await();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
number = 2;
condition2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printB() {
lock.lock();
try {
if (number != 2) {
condition2.await();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
number = 3;
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printC() {
lock.lock();
try {
if (number != 3) {
condition3.await();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + number);
number = 1;
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}